Understanding GERD (Acid Reflux): Causes, Symptoms & Effective Treatments
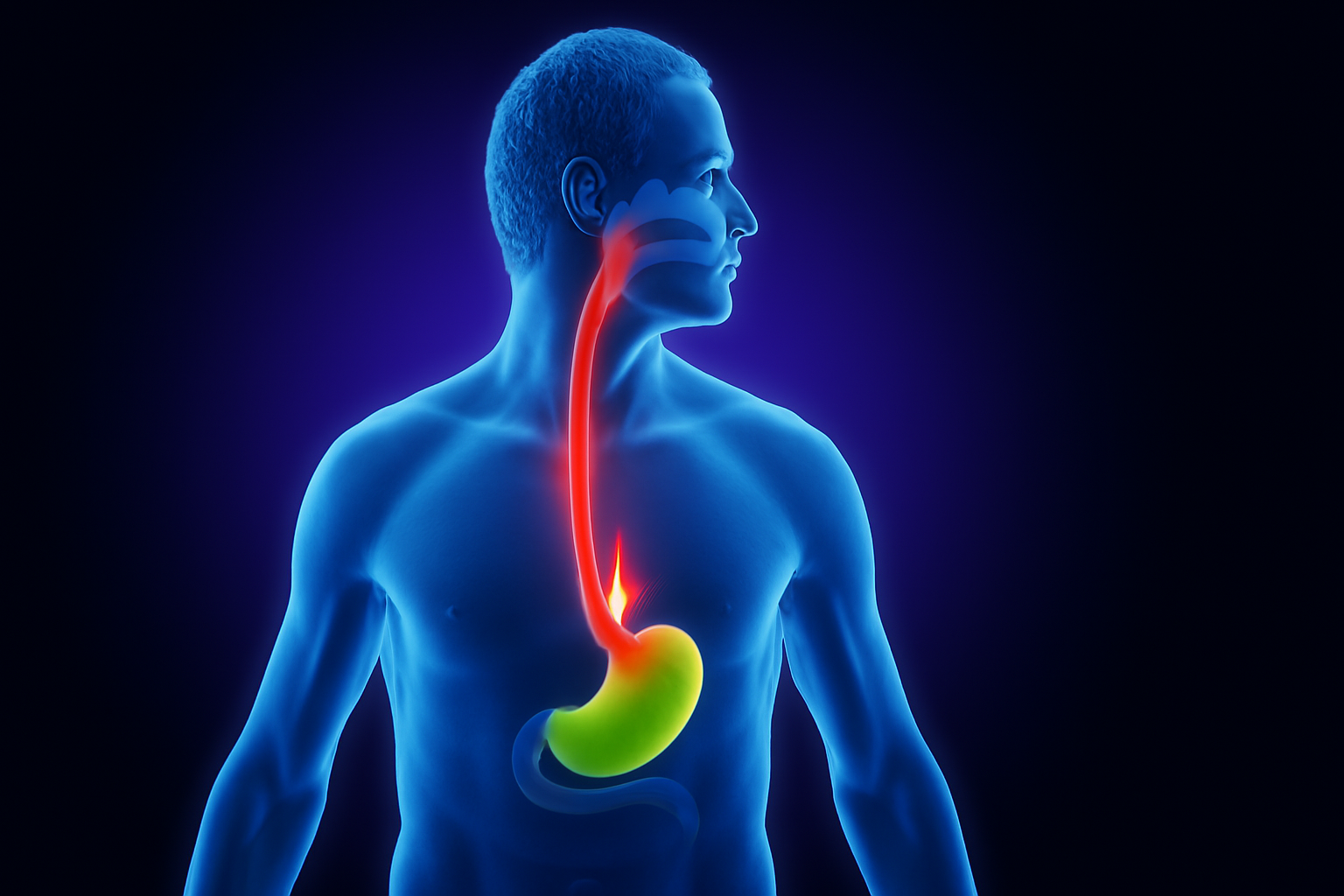
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), commonly known as acid reflux, is a digestive disorder where stomach acid frequently flows back into the tube connecting your mouth and stomach (esophagus). This backwash (acid reflux) can irritate the lining of your esophagus and cause persistent discomfort.
What Causes GERD?
GERD occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a ring of muscle that acts as a valve between the stomach and esophagus, weakens or relaxes inappropriately. Factors contributing to GERD include obesity, hiatal hernia, certain foods (spicy, fatty, citrus, chocolate), smoking, and pregnancy.
Common Symptoms of GERD
- Heartburn — a burning sensation in the chest, often after eating, which might worsen at night or when lying down
- Regurgitation of food or sour liquid
- Difficulty swallowing
- Chest pain
- Chronic cough or throat irritation
Diagnosing GERD
Diagnosis involves reviewing clinical symptoms and might include tests such as endoscopy, pH monitoring, and esophageal manometry to assess acid reflux and esophageal function.
Treatment Options for GERD
Lifestyle and Dietary Changes
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Eat smaller meals more frequently
- Avoid trigger foods like citrus, fatty or spicy foods, chocolate, caffeine, alcohol, and peppermint
- Do not lie down for 2-3 hours after eating
- Elevate the head of your bed by 6 inches to prevent nighttime reflux
- Quit smoking
Medications
Over-the-counter and prescription medications can reduce acid production and heal the esophagus. These include:
- Antacids to neutralize stomach acid
- H-2 receptor blockers (like famotidine, cimetidine)
- Proton pump inhibitors (such as omeprazole, lansoprazole)
Consult your healthcare provider before starting any medications to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
Surgical Options
If symptoms persist or complications arise, surgery such as fundoplication may be recommended. This procedure strengthens the LES to prevent acid reflux.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical advice if you experience frequent heartburn, difficulty swallowing, unexplained weight loss, or chest pain, as untreated GERD can lead to more serious complications.
Managing GERD effectively improves quality of life and prevents long-term damage. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are key.
